A Comprehensive Guide to ATO, MTS, MTO, ETO, and CTO
In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, choosing the right production model can make or break your operational efficiency. Whether you’re a manufacturing executive, operations manager, or business owner looking to optimize your processes, understanding the five key production models is essential for making informed decisions about your ERP implementation.
This guide breaks down the five major manufacturing production models to help you identify which approach best suits your business needs:
- Assembly to Order (ATO)
- Make to Stock (MTS)
- Make to Order (MTO)
- Engineer to Order (ETO)
- Configure to Order (CTO)
Why Production Models Matter in Manufacturing

Inventory costs and production efficiency. The production model you choose directly impacts:
- How you manage inventory
- Your ability to customize products
- Production lead times
- Supply chain requirements
- Overall operational costs
By selecting the right production model for your specific manufacturing environment, you can streamline operations, reduce costs, and better meet customer expectations.
Overview of Each Production Model
Assembly to Order (ATO): Flexibility Meets Efficiency
What is ATO?
The Assembly to Order model represents a middle ground between customization and standardization. In this approach, manufacturers maintain an inventory of components or subassemblies rather than finished products. When a customer places an order, these components are assembled into the final product according to specific requirements.
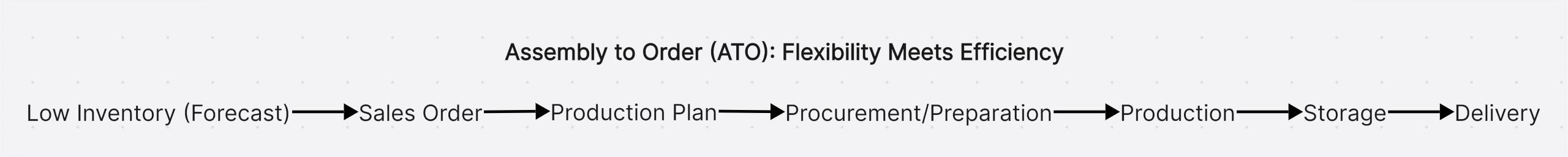
Key Characteristics
- Component Standardization: Uses standardized components that can be assembled in different configurations
- Customization Level: Moderate customization through different component combinations
- Inventory Focus: Component-level rather than finished goods
- Lead Time: Moderate (shorter than MTO but longer than MTS)
- Production Trigger: Customer orders initiate final assembly
Ideal For
ATO works best for manufacturers who:
- Offer products with multiple configuration options
- Need to balance customization with reasonable delivery times
- Have products composed of standard components that can be assembled in various ways
- Serve markets where customers expect some customization but aren’t willing to wait for complete custom manufacturing
Real-World Example
Computer manufacturers often use the ATO model. They stock standard components (processors, memory, hard drives) and assemble them based on customer specifications when orders come in.
Business Impact
- Inventory Efficiency: Reduces finished goods inventory while maintaining component-level stock
- Customer Satisfaction: Offers customization without excessive lead times
- Operational Complexity: Requires sophisticated component inventory management
- Financial Considerations: Moderate inventory carrying costs, focused on components
Make to Stock (MTS): Optimized for Speed and Volume
What is MTS?
The Make to Stock model is the traditional manufacturing approach where products are manufactured in advance based on forecasted demand and stored as finished goods inventory. When customers place orders, products are shipped directly from existing stock.

Key Characteristics
- Standardization: High standardization with fixed specifications
- Customization Level: Minimal to none
- Inventory Focus: Finished goods inventory
- Lead Time: Very short (immediate availability)
- Production Trigger: Forecast-driven production schedules
Ideal For
MTS works best for manufacturers who:
- Produce standard items with predictable demand
- Compete in markets where immediate availability is crucial
- Make products with longer shelf lives and slower iteration cycles
- Have high-volume production of relatively low-cost items
Real-World Example

Consumer packaged goods manufacturers typically use MTS. Companies producing standard household items like detergent or paper towels manufacture based on sales forecasts and stock retail channels with finished products.
Business Impact
- Inventory Efficiency: Higher finished goods inventory but immediate fulfillment capability
- Customer Satisfaction: Instant availability but limited customization
- Operational Complexity: Requires accurate demand forecasting
- Financial Considerations: Higher inventory carrying costs but economies of scale in production
Make to Order (MTO): Customization Without Waste
What is MTO?
In the Make to Order model, production begins only after a confirmed customer order is received. While raw materials may be stocked, the manufacturing process doesn’t start until specific customer requirements are known.

Key Characteristics
- Standardization: Moderate standardization with customization options
- Customization Level: Significant customization within product parameters
- Inventory Focus: Raw materials and some common components
- Lead Time: Longer (includes full production time)
- Production Trigger: Customer orders initiate production
Ideal For
MTO works best for manufacturers who:
- Offer products that require significant customization
- Serve markets where customers are willing to wait for customized products
- Want to minimize finished goods inventory
- Need flexibility to adapt to changing customer requirements
Real-World Example

Custom furniture manufacturers typically use MTO. They may stock wood, fabric, and hardware, but don’t begin building a piece until a customer places an order with specific requirements.
Business Impact
- Inventory Efficiency: Minimal finished goods inventory, reducing carrying costs
- Customer Satisfaction: High customization but longer lead times
- Operational Complexity: Requires flexible production scheduling
- Financial Considerations: Lower inventory costs but potentially higher production costs per unit
Engineer to Order (ETO): Ultimate Customization

What is ETO?
The Engineer to Order model represents the highest level of customization, where products are designed, engineered, and manufactured specifically for individual customer requirements. This approach is used for complex, unique products that require specialized design work.
Key Characteristics
- Standardization: Minimal standardization, often completely custom designs
- Customization Level: Complete customization from design through production
- Inventory Focus: Raw materials only, often procured specifically for each project
- Lead Time: Very long (includes design, engineering, and production)
- Production Trigger: Customer specifications require new design work
Ideal For
ETO works best for manufacturers who:
- Create highly specialized, complex products
- Serve markets where unique solutions are required
- Work on large-scale, high-value projects
- Have strong engineering and design capabilities
Real-World Example

Aerospace manufacturers often use ETO for specialized equipment. When an airline needs custom components for a specific aircraft model, the manufacturer designs and builds these components to exact specifications.
Business Impact
- Inventory Efficiency: Minimal inventory requirements, often project-specific procurement
- Customer Satisfaction: Highest level of customization but longest lead times
- Operational Complexity: Requires sophisticated project management and engineering resources
- Financial Considerations: Higher margins but also higher costs per unit and project management overhead
Configure to Order (CTO): Structured Customization
What is CTO?
The Configure to Order model evolved from ATO but offers more structured customization options. Products are designed with modular components and predefined configuration options, allowing customers to select from established parameters rather than unlimited customization.
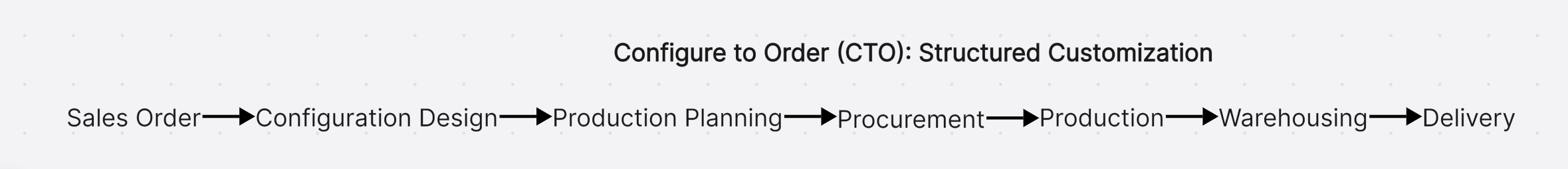
Key Characteristics
- Standardization: Standardized modules with predefined configuration options
- Customization Level: Significant customization within defined parameters
- Inventory Focus: Modular components and subassemblies
- Lead Time: Moderate (similar to ATO)
- Production Trigger: Customer configuration selections
Ideal For
CTO works best for manufacturers who:
- Offer complex products with multiple configuration options
- Need to balance customization with production efficiency
- Have modular product designs
- Serve markets where customers expect customization within reasonable timeframes
Real-World Example

Automobile manufacturers often use CTO. Customers can select from predefined options for features, colors, and packages, but all within the manufacturer’s established parameters.
Business Impact
- Inventory Efficiency: Focused on modular components rather than finished goods
- Customer Satisfaction: Perceived high customization with manageable lead times
- Operational Complexity: Requires sophisticated product configuration systems
- Financial Considerations: Moderate inventory costs with premium pricing for customization
Comparing the Five Production Models
| Aspect | ATO | MTS | MTO | ETO | CTO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customization | Moderate | Minimal | Significant | Complete | Significant within parameters |
| Lead Time | Moderate | Immediate | Long | Very Long | Moderate |
| Inventory Level | Components | Finished Goods | Raw Materials | Project-Specific | Modular Components |
| Production Trigger | Customer Order | Forecast | Customer Order | Customer Specifications | Customer Configuration |
| Cost Structure | Moderate unit cost | Lower unit cost | Higher unit cost | Highest unit cost | Moderate to high unit cost |
| Business Scale | $20M-$500M | $20M-$500M | $20M-$500M | $20M-$500M | $100M-$1B |
| Typical Industry | Electronics, Computers | Consumer Goods | Furniture, Custom Manufacturing | Aerospace, Specialized Equipment | Automotive, Industrial Equipment |
Choosing the Right Production Model for Your Business
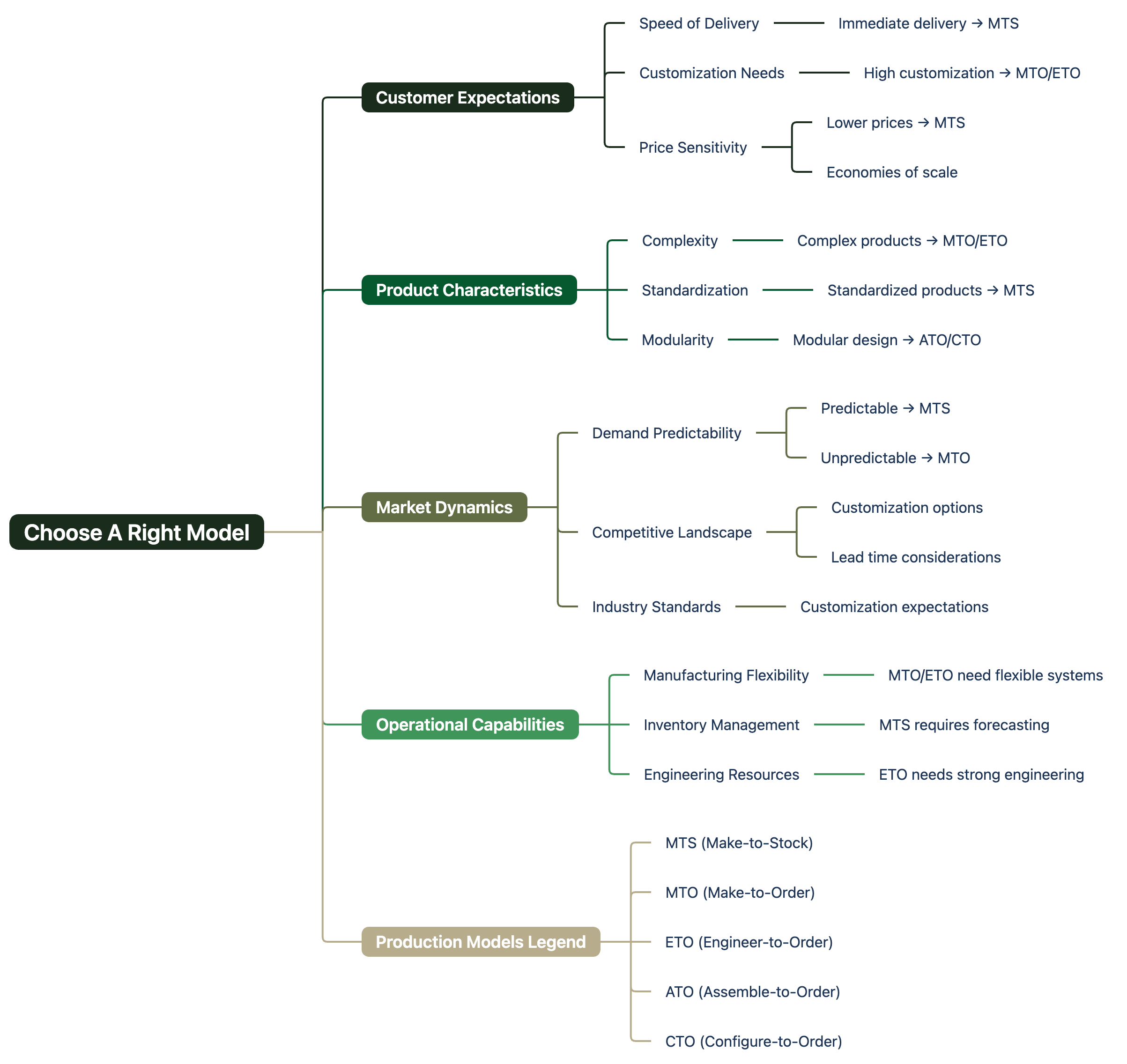
Selecting the optimal production model depends on several factors:
Customer Expectations
- Speed of Delivery: If customers expect immediate delivery, MTS may be necessary
- Customization Needs: Higher customization requirements point toward MTO or ETO
- Price Sensitivity: MTS typically offers lower prices due to economies of scale
Product Characteristics
- Complexity: More complex products often require MTO or ETO approaches
- Standardization Potential: Products that can be standardized work well with MTS
- Modularity: Modular products are ideal for ATO or CTO
Market Dynamics
- Demand Predictability: Predictable demand favors MTS; unpredictable demand suits MTO
- Competitive Landscape: Consider what your competitors offer in terms of customization and lead time
- Industry Standards: Some industries have established expectations for customization
Operational Capabilities
- Manufacturing Flexibility: MTO and ETO require more flexible production systems
- Inventory Management: MTS requires robust forecasting and inventory management
- Engineering Resources: ETO demands strong engineering and design capabilities
Implementing Your Chosen Production Model with ERP
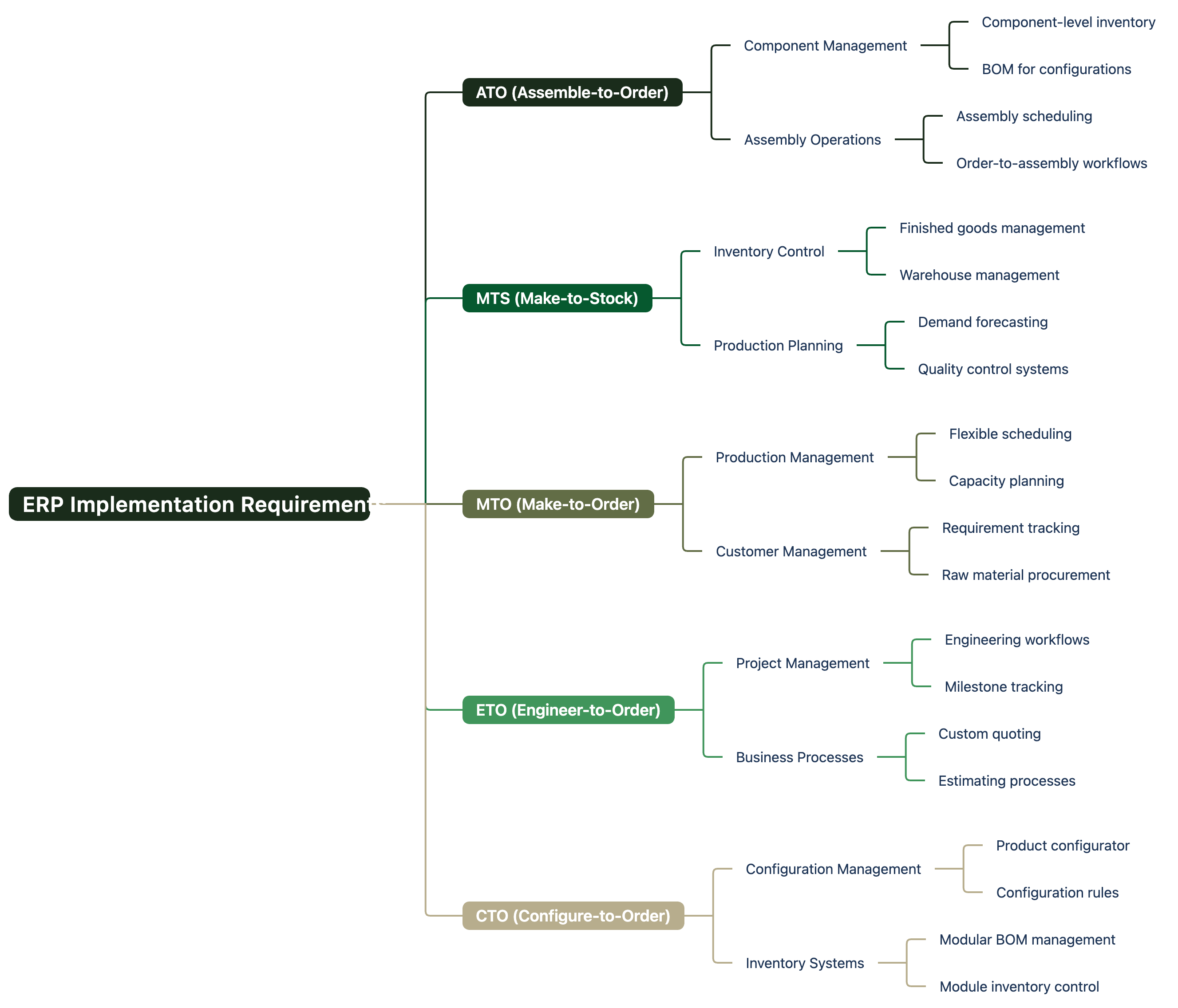
Once you’ve identified the right production model, implementing it effectively requires robust ERP support:
For ATO Implementation:
- Focus on component-level inventory management
- Implement efficient assembly scheduling
- Develop a clear bill of materials (BOM) for various configurations
- Create streamlined order-to-assembly workflows
For MTS Implementation:
- Invest in demand forecasting capabilities
- Optimize inventory management for finished goods
- Implement efficient warehouse management
- Develop robust quality control for consistent production
For MTO Implementation:
- Create flexible production scheduling systems
- Implement customer requirement management
- Develop efficient raw material procurement processes
- Focus on production capacity planning
For ETO Implementation:
- Implement project management capabilities
- Develop engineering and design workflows
- Create custom quoting and estimating processes
- Implement milestone-based production tracking
For CTO Implementation:
- Develop product configurator systems
- Implement modular BOM management
- Create efficient module inventory management
- Develop clear configuration rules and constraints
The Future of Manufacturing Production Models
As technology continues to evolve, manufacturing production models are also transforming:
- Digital Twins: Virtual representations of physical products, enabling better customization in all models
- AI-Driven Forecasting: Improving MTS accuracy through better demand prediction
- Additive Manufacturing: Enabling more cost-effective customization for MTO and ETO
- IoT Integration: Providing real-time production data across all models
- Hybrid Approaches: Many manufacturers now implement multiple models for different product lines
The most successful manufacturers are increasingly adopting flexible approaches that combine elements of different production models, supported by sophisticated ERP systems that can handle this complexity.
Conclusion
Understanding the five manufacturing production models—ATO, MTS, MTO, ETO, and CTO—is essential for optimizing your manufacturing operations. Each model offers distinct advantages and challenges, and the right choice depends on your specific business requirements, customer expectations, and operational capabilities.
By aligning your production model with your business strategy and implementing it effectively through appropriate ERP systems, you can achieve the optimal balance of customization, lead time, inventory costs, and operational efficiency.
Ready to Optimize Your Manufacturing Operations?
Now that you understand the five key manufacturing production models, it’s time to take your operations to the next level with the right tools and resources.
Introducing the MTO Template
For manufacturers implementing the Make-to-Order (MTO) production model, we’re excited to offer our specialized MTO template designed to streamline your operations. This ready-to-use template helps you:
- Efficiently manage customer orders and specifications
- Optimize your production scheduling
- Track raw materials and component inventory
- Coordinate your supply chain more effectively
- Monitor production progress in real-time
[Install the MTO Template Now] and transform your manufacturing operations with a solution specifically designed for Make-to-Order environments.
Looking for Other Production Model Templates?
While our MTO template is currently available, we understand that your business might operate under a different production model. We’re actively developing templates for ATO, MTS, ETO, and CTO production models to serve the diverse needs of the manufacturing community.
Join our waitlist today to be the first to know when new templates become available:
- ATO Template: Perfect for assembly-focused operations with component inventories
- MTS Template: Ideal for forecast-driven production with finished goods inventory
- ETO Template: Designed for custom engineering and project-based manufacturing
- CTO Template: Optimized for modular configuration and structured customization
[Join the Waitlist] and we’ll notify you as soon as these additional templates are released.
Need Custom Manufacturing Solutions?
Every manufacturing operation is unique. If you need a customized solution tailored to your specific production environment, our team of manufacturing experts is ready to help.
[Contact Our Team] for a personalized consultation and discover how we can help you implement the perfect production model for your business.
Don’t let outdated production models hold your manufacturing business back. Take the first step toward operational excellence today!



